Derivation of Sum and Difference of Two Angles
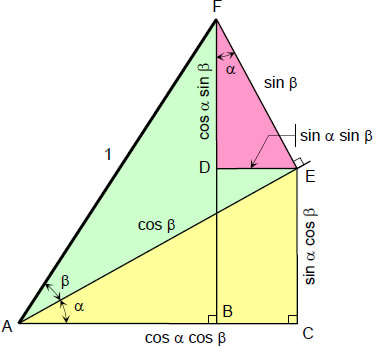
 The sum and difference of two angles can be derived from the figure shown below.
The sum and difference of two angles can be derived from the figure shown below.
Consider triangle AEF:
$\cos \beta = \dfrac{\overline{AE}}{1}; \,\, \overline{AE} = \cos \beta$
$\sin \beta = \dfrac{\overline{EF}}{1}; \,\, \overline{EF} = \sin \beta$
From triangle EDF:
$\sin \alpha = \dfrac{\overline{DE}}{\overline{EF}}$
$\sin \alpha = \dfrac{\overline{DE}}{\sin \beta}$
$\overline{DE} = \sin \alpha \, \sin \beta$
$\cos \alpha = \dfrac{\overline{DF}}{\overline{EF}}$
$\cos \alpha = \dfrac{\overline{DF}}{\sin \beta}$
$\overline{DF} = \cos \alpha \, \sin \beta$
$\overline{BC} = \overline{DE} = \sin \alpha \, \sin \beta$
From Triangle ACE:
$\sin \alpha = \dfrac{\overline{CE}}{\overline{AE}}$
$\sin \alpha = \dfrac{\overline{CE}}{\cos \beta}$
$\overline{CE} = \sin \alpha \, \cos \beta$
$\cos \alpha = \dfrac{\overline{AC}}{\overline{AE}}$
$\cos \alpha = \dfrac{\overline{AC}}{\cos \beta}$
$\overline{AC} = \cos \alpha \, \cos \beta$
$\overline{BD} = \overline{CE} = \sin \alpha \, \cos \beta$
The summary of the above solution is shown below:
Sum of two angles
From triangle ABF:
$\sin (\alpha + \beta) = \overline{BD} + \overline{DF}$
$\cos (\alpha + \beta) = \overline{AC} - \overline{BC}$
$\tan (\alpha + \beta) = \dfrac{\sin (\alpha + \beta)}{\cos (\alpha + \beta)}$
$\tan (\alpha + \beta) = \dfrac{\sin \alpha \, \cos \beta + \cos \alpha \, \sin \beta}{\cos \alpha \, \cos \beta - \sin \alpha \, \sin \beta}$
$\tan (\alpha + \beta) = \dfrac{\dfrac{\sin \alpha \, \cos \beta}{\cos \alpha \, \cos \beta} + \dfrac{\cos \alpha \, \sin \beta}{\cos \alpha \, \cos \beta}}{\dfrac{\cos \alpha \, \cos \beta}{\cos \alpha \, \cos \beta} - \dfrac{\sin \alpha \, \sin \beta}{\cos \alpha \, \cos \beta}}$
$\tan (\alpha + \beta) = \dfrac{\dfrac{\sin \alpha}{\cos \alpha} + \dfrac{\sin \beta}{\cos \beta}}{1 - \dfrac{\sin \alpha}{\cos \alpha} \, \dfrac{\sin \beta}{\cos \beta}}$
Difference of two angles
Let β = -β and note that
sin (-β) = -sin β
cos (-β) = cos β and
tan (-β) = -tan β
$\sin [ \, \alpha + (-\beta) \, ] = \sin \alpha \, \cos (-\beta) + \cos \alpha \, \sin (-\beta)$
$\cos [ \, \alpha + (-\beta) \, ] = \cos \alpha \, \cos (-\beta) - \sin \alpha \, \sin (-\beta)$
$\tan [ \, \alpha + (-\beta) \, ] = \dfrac{\tan \alpha + \tan (-\beta)}{1 - \tan \alpha \, \tan (-\beta)}$
