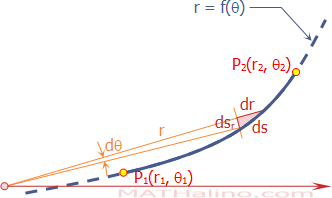
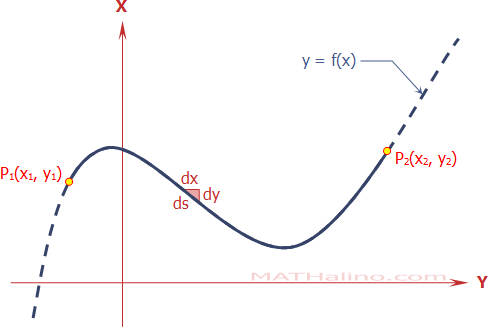
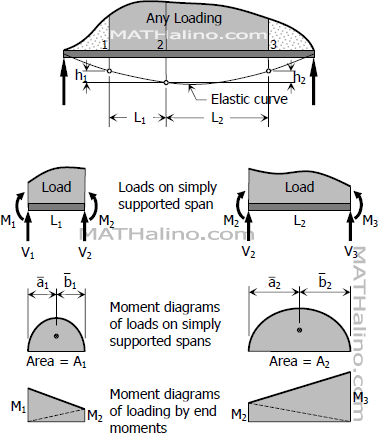
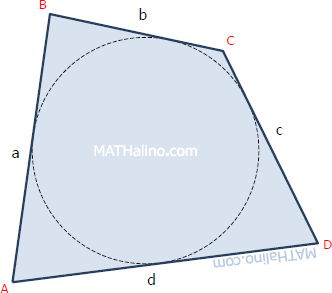
Derivation of Product of First n Terms of Geometric Progression
The product of the first $n$ terms of a Geometric Progression is given by the following:
Given the first term $a_1$ and last term $a_n$:
Given the first term $a_1$ and the common ratio $r$