Laplace Transform by Direct Integration
To get the Laplace transform of the given function $f(t)$, multiply $f(t)$ by $e^{-st}$ and integrate with respect to $t$ from zero to infinity. In symbol,
- Read more about Laplace Transform by Direct Integration
- Log in or register to post comments
Laplace Transform
Definition of Laplace Transform
Let $f(t)$ be a given function which is defined for $t \ge 0$. If there exists a function $F(s)$ so that
then $F(s)$ is called the Laplace Transform of $f(t)$, and will be denoted by $\mathcal{L} \left\{f(t)\right\}$. Notice the integrator $e^{-st} \, dt$ where $s$ is a parameter which may be real or complex.
- Read more about Laplace Transform
- 1 comment
- Log in or register to post comments
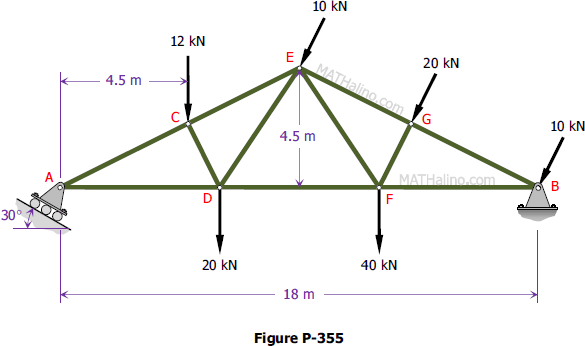
Problem 355 | Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent Force System
Problem 355
Determine the reactions at A and B on the Fink truss shown in Fig. P-355. Members CD and FG are respectively perpendicular to AE and BE at their midpoints.
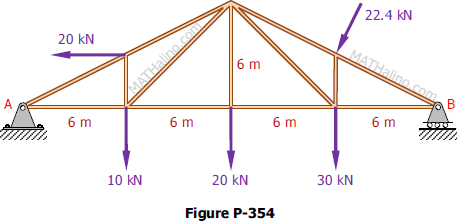
Problem 354 | Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent Force System
Problem 354
Compute the total reactions at A and B on the truss shown in Fig. P-354.
Problem 353 | Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent Force System
Problem 353
The forces acting on a 1-m length of a dam are shown in Fig. P-353. The upward ground reaction varies uniformly from an intensity of p1 kN/m to p2 kN/m at B. Determine p1 and p2 and also the horizontal resistance to sliding.

Problem 352 | Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent Force System
Problem 352
A pulley 4 ft in diameter and supporting a load 200 lb is mounted at B on a horizontal beam as shown in Fig. P-352. The beam is supported by a hinge at A and rollers at C. Neglecting the weight of the beam, determine the reactions at A and C.

Problem 04 | Exact Equations
- Read more about Problem 04 | Exact Equations
- Log in or register to post comments

Recent comments