Problem 07 | Separation of Variables
Problem 07
$y' = x \exp (y - x^2)$, when $x = 0$, $y = 0$.
Solution 07
Click here to expand or collapse this section
$\dfrac{dy}{dx} = x e^{y - x^2}$
- Read more about Problem 07 | Separation of Variables
- Log in or register to post comments
Problem 05 | Separation of Variables
Problem 05
$2y \, dx = 3x \, dy$, when $x = -2$, $y = 1$.
Solution 05
From Solution 04,
$\dfrac{x^2}{y^3} = c$
- Read more about Problem 05 | Separation of Variables
- Log in or register to post comments
Problem 03 | Separation of Variables
Problem 03
$xy \, y' = 1 + y^2$, when $x = 2$, $y = 3$.
Solution 03
$xy \, y' = 1 + y^2$
$xy \dfrac{dy}{dx} = 1 + y^2$
- Read more about Problem 03 | Separation of Variables
- Log in or register to post comments
Problem 02 | Separation of Variables
Problem 02
$2xy \, y' = 1 + y^2$, when $x = 2$, $y = 3$.
Solution 2
$2xy \, y' = 1 + y^2$
$2xy \dfrac{dy}{dx} = 1 + y^2$
- Read more about Problem 02 | Separation of Variables
- Log in or register to post comments
Problem 04 | Separation of Variables
Problem 04
$2y \, dx = 3x \, dy$, when $x = 2$, $y = 1$.
Solution 04
$2y \, dx = 3x \, dy$
$\dfrac{2y \, dx}{xy} = \dfrac{3x \, dy}{xy}$
- Read more about Problem 04 | Separation of Variables
- Log in or register to post comments
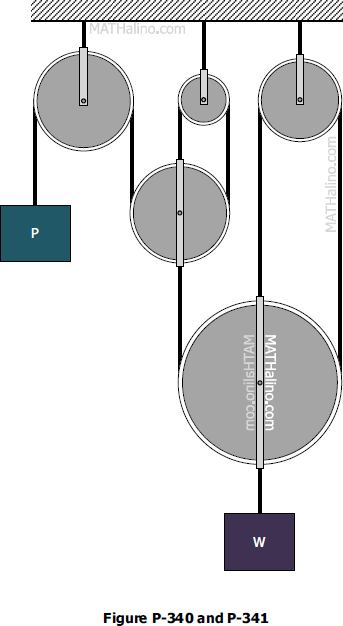
Problem 340 - 341 | Equilibrium of Parallel Force System
Problem 340
For the system of pulleys shown in Fig. P-340, determine the ratio of W to P to maintain equilibrium. Neglect axle friction and the weights of the pulleys.
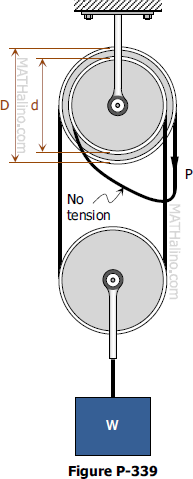
Problem 339 | Equilibrium of Parallel Force System
Problem 339
The differential chain hoist shown in Fig. P-339 consists of two concentric pulleys rigidly fastened together. The pulleys form two sprockets for an endless chain looped over them in two loops. In one loop is mounted a movable pulley supporting a load W. Neglecting friction, determine the maximum load W that can just be raised by a pull P supplied as shown.
- Read more about Problem 339 | Equilibrium of Parallel Force System
- Log in or register to post comments
Quadratic Equations in One Variable
Quadratic Equation
Quadratic equation is in the form
Where
a, b, & c = real-number constants
a & b = numerical coefficient or simply coefficients
a = coefficient of x2
b = coefficient of x
c = constant term or simply constant
a cannot be equal to zero while either b or c can be zero
- Read more about Quadratic Equations in One Variable
- Log in or register to post comments

Recent comments