Frustum of a Regular Pyramid
Frustum of a regular pyramid is a portion of right regular pyramid included between the base and a section parallel to the base.
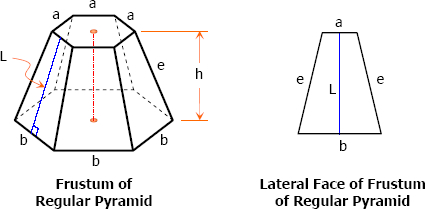
Properties of a Frustum of Regular Pyramid
- The slant height of a frustum of a regular pyramid is the altitude of the face.
- The lateral edges of a frustum of a regular pyramid are equal, and the faces are equal isosceles trapezoids.
- The bases of a frustum of a regular pyramid are similar regular polygons. If these polygons become equal, the frustum will become prism.
Elements of a Frustum of Regular Pyramid
a = upper base edge
b = lower base edge
e = lateral edge
h = altitude
L = slant height
A1 = area of lower base
A2 = area of upper base
n = number of lower base edges
Formulas for Frustum of a Regular Pyramid
See the formulas of regular polygon for the formula of A1 and A2
Volume
See the derivation of formula for volume of a frustum.
Lateral Area, AL
The lateral area of frustum of regular pyramid is equal to one-half the sum of the perimeters of the bases multiplied by the slant height.
The relationship between slant height L, lower base edge b, upper base edge a, and lateral edge e, of the frustum of regular pyramid is given by
