Centers of a Triangle
This page will define the following: incenter, circumcenter, orthocenter, centroid, and Euler line.
Incenter
Incenter is the center of the inscribed circle (incircle) of the triangle, it is the point of intersection of the angle bisectors of the triangle.

The radius of incircle is given by the formula
where At = area of the triangle and s = ½ (a + b + c). See the derivation of formula for radius of incircle.
Circumcenter
Circumcenter is the point of intersection of perpendicular bisectors of the triangle. It is also the center of the circumscribing circle (circumcircle).
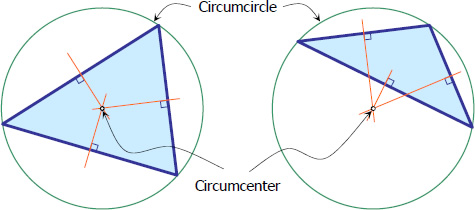
As you can see in the figure above, circumcenter can be inside or outside the triangle. In the case of the right triangle, circumcenter is at the midpoint of the hypotenuse. Given the area of the triangle At, the radius of the circumscribing circle is given by the formula
You may want to take a look for the derivation of formula for radius of circumcircle.
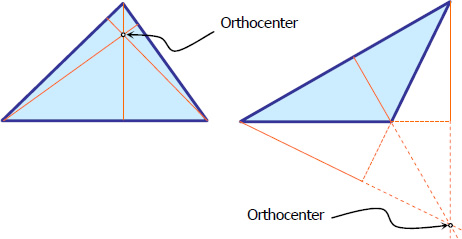
Orthocenter
Orthocenter of the triangle is the point of intersection of the altitudes. Like circumcenter, it can be inside or outside the triangle as shown in the figure below.
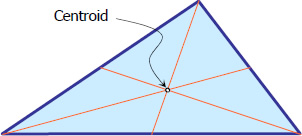
Centroid
The point of intersection of the medians is the centroid of the triangle. Centroid is the geometric center of a plane figure.
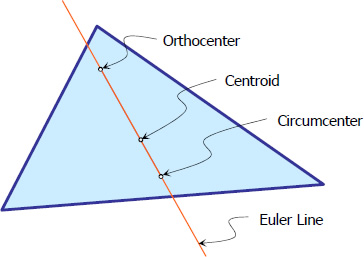
Euler Line
The line that would pass through the orthocenter, circumcenter, and centroid of the triangle is called the Euler line.