Solution to Problem 686 | Beam Deflection by Method of Superposition
Problem 686
Determine the value of EIδ under each concentrated load in Fig. P-686.
Solution to Problem 685 | Beam Deflection by Method of Superposition
Problem 685
Determine the midspan value of EIδ for the beam loaded as shown in Fig. P-685. Use the method of superposition.
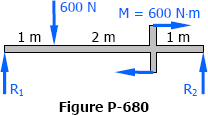
Solution to Problem 674 | Midspan Deflection
Problem 674
Find the deflection midway between the supports for the overhanging beam shown in Fig. P-674.

- Read more about Solution to Problem 674 | Midspan Deflection
- Log in or register to post comments
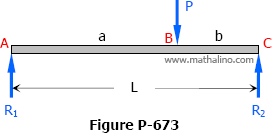
Solution to Problem 673 | Midspan Deflection
Problem 673
For the beam shown in Fig. P-673, show that the midspan deflection is δ = (Pb/48EI) (3L2 - 4b2).
- Read more about Solution to Problem 673 | Midspan Deflection
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 668 | Deflections in Simply Supported Beams
Problem 668
For the beam shown in Fig. P-668, compute the value of P that will cause the tangent to the elastic curve over support R2 to be horizontal. What will then be the value of EIδ under the 100-lb load?

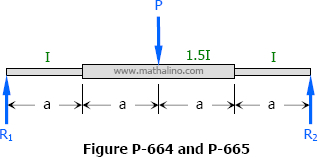
Solution to Problem 664 | Deflections in Simply Supported Beams
Problem 664
The middle half of the beam shown in Fig. P-664 has a moment of inertia 1.5 times that of the rest of the beam. Find the midspan deflection. (Hint: Convert the M diagram into an M/EI diagram.)
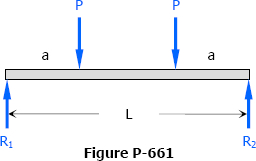
Solution to Problem 661 | Deflections in Simply Supported Beams
Problem 661
Compute the midspan deflection of the symmetrically loaded beam shown in Fig. P-661. Check your answer by letting a = L/2 and comparing with the answer to Problem 609.
Solution to Problem 659 | Deflections in Simply Supported Beams
Problem 659
A simple beam supports a concentrated load placed anywhere on the span, as shown in Fig. P-659. Measuring x from A, show that the maximum deflection occurs at x = √[(L2 - b2)/3].