Solution to Problem 236 Statically Indeterminate
Problem 236
A rigid block of mass M is supported by three symmetrically spaced rods as shown in Fig. P-236. Each copper rod has an area of 900 mm2; E = 120 GPa; and the allowable stress is 70 MPa. The steel rod has an area of 1200 mm2; E = 200 GPa; and the allowable stress is 140 MPa. Determine the largest mass M which can be supported.
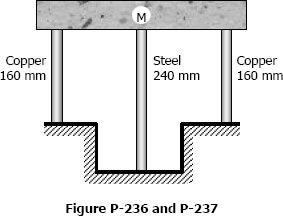
- Read more about Solution to Problem 236 Statically Indeterminate
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 235 Statically Indeterminate
Problem 235
A timber column, 8 in. × 8 in. in cross section, is reinforced on each side by a steel plate 8 in. wide and t in. thick. Determine the thickness t so that the column will support an axial load of 300 kips without exceeding a maximum timber stress of 1200 psi or a maximum steel stress of 20 ksi. The moduli of elasticity are 1.5 × 106 psi for timber, and 29 × 106 psi for steel.
- Read more about Solution to Problem 235 Statically Indeterminate
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 233 Statically Indeterminate
Problem 233
A steel bar 50 mm in diameter and 2 m long is surrounded by a shell of a cast iron 5 mm thick. Compute the load that will compress the combined bar a total of 0.8 mm in the length of 2 m. For steel, E = 200 GPa, and for cast iron, E = 100 GPa.
- Read more about Solution to Problem 233 Statically Indeterminate
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 226 Biaxial Deformation
Problem 226
A 2-in.-diameter steel tube with a wall thickness of 0.05 inch just fits in a rigid hole. Find the tangential stress if an axial compressive load of 3140 lb is applied. Assume ν = 0.30 and neglect the possibility of buckling.
- Read more about Solution to Problem 226 Biaxial Deformation
- 2 comments
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 225 Biaxial Deformation
Problem 225
A welded steel cylindrical drum made of a 10-mm plate has an internal diameter of 1.20 m. Compute the change in diameter that would be caused by an internal pressure of 1.5 MPa. Assume that Poisson's ratio is 0.30 and E = 200 GPa.
- Read more about Solution to Problem 225 Biaxial Deformation
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 223 Triaxial Deformation
Problem 223
- Read more about Solution to Problem 223 Triaxial Deformation
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 211 Axial Deformation
Problem 211
A bronze bar is fastened between a steel bar and an aluminum bar as shown in Fig. p-211. Axial loads are applied at the positions indicated. Find the largest value of P that will not exceed an overall deformation of 3.0 mm, or the following stresses: 140 MPa in the steel, 120 MPa in the bronze, and 80 MPa in the aluminum. Assume that the assembly is suitably braced to prevent buckling. Use Est = 200 GPa, Eal = 70 GPa, and Ebr = 83 GPa.
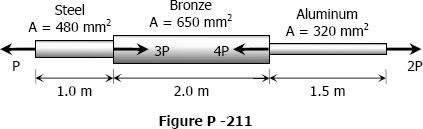
- Read more about Solution to Problem 211 Axial Deformation
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 141 Pressure Vessel
Problem 141
The tank shown in Fig. P-141 is fabricated from 1/8-in steel plate. Calculate the maximum longitudinal and circumferential stress caused by an internal pressure of 125 psi.
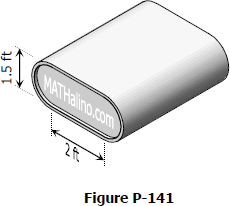
- Read more about Solution to Problem 141 Pressure Vessel
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 139 Pressure Vessel
Problem 139
Find the limiting peripheral velocity of a rotating steel ring if the allowable stress is 20 ksi and steel weighs 490 lb/ft3. At what revolutions per minute (rpm) will the stress reach 30 ksi if the mean radius is 10 in.?
- Read more about Solution to Problem 139 Pressure Vessel
- Log in or register to post comments
