Derivation of Formula for the Future Amount of Ordinary Annuity
The sum of ordinary annuity is given by
To learn more about annuity, see this page: ordinary annuity, deferred annuity, annuity due, and perpetuity.
Derivation
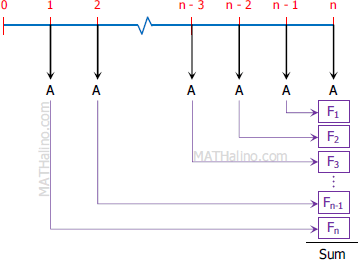
$F = \text{ Sum}$
$F = A + F_1 + F_2 + F_3 + \cdots + F_{n-1} + F_n$
$F = A + A(1 + i) + A(1 + i)^2 + A(1 + i)^3 + \cdots + A(1 + i)^{n-1} + A(1 + i)^n$
The sum above forms a geometric progression, GP. The formula for the sum of GP is given by
$S = \dfrac{a_1(r^n - 1)}{r - 1}$
Where
Sum, S = F
First term, a1 = A
Common ratio, r = (1 + i)
Number of terms, n = number of payments, n
Substitute,
$F = \dfrac{A[ \, (1 + i)^n - 1 \, ]}{(1 + i) - 1}$
$F = \dfrac{A[ \, (1 + i)^n - 1 \, ]}{i}$
It is important to note that the power n is number of payments not number of compounding periods. Also note that for ordinary annuity, the number of payments and number of compounding periods are both equal to n.
