Example 04: Required Depth of Rectangular Timber Beam Based on Allowable Bending, Shear, and Deflection
Problem
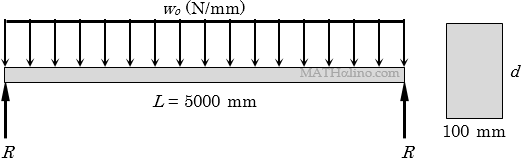
A beam 100 mm wide is to be loaded with 3 kN concentrated loads spaced uniformly at 0.40 m on centers throughout the 5 m span. The following data are given:
Allowable shear stress = 1.24 MPa
Allowable deflection = 1/240 of span
Modulus of elasticity = 18,600 MPa
Weight of wood = 8 kN/m3
- Find the depth d considering bending stress only.
- Determine the depth d considering shear stress only.
- Calculate the depth d considering deflection only.