March 2017
Influence Lines for Beams
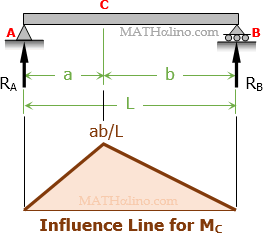
A downward concentrated load of magnitude 1 unit moves across the simply supported beam AB from A to B. We wish to determine the following functions:
- reaction at A
- reaction at B
- shear at C and
- moment at C
when the unit load is at a distance x from support A. Since the value of the above functions will vary according to the location of the unit load, the best way to represent these functions is by influence diagram.
- Read more about Influence Lines for Beams
- Log in or register to post comments
Influence Lines
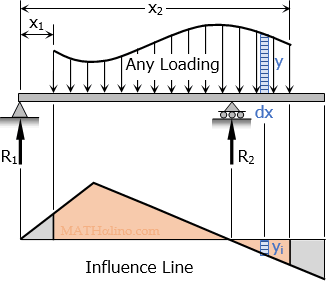
Influence line is the graphical representation of the response function of the structure as the downward unit load moves across the structure. The ordinate of the influence line show the magnitude and character of the function.
The most common response functions of our interest are support reaction, shear at a section, bending moment at a section, and force in truss member.
With the aid of influence diagram, we can...
- determine the position of the load to cause maximum response in the function.
- calculate the maximum value of the function.
Value of the function for any type of load
$\displaystyle \text{Function} = \int_{x_1}^{x_2} y_i (y \, dx)$
- Read more about Influence Lines
- Log in or register to post comments
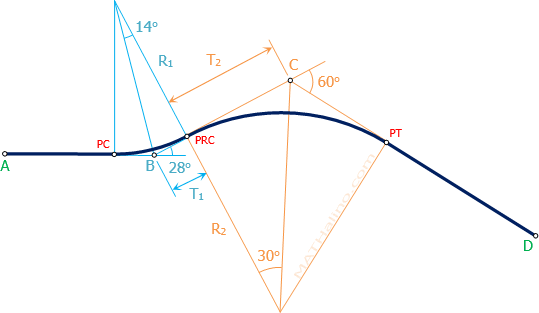
Reversed Curve to Connect Three Traversed Lines
Situation
A reversed curve with diverging tangent is to be designed to connect to three traversed lines for the portion of the proposed highway. The lines AB is 185 m, BC is 122.40 m, and CD is 285 m. The azimuth are Due East, 242°, and 302° respectively. The following are the cost index and specification:
Number of Lanes = Two Lanes
Width of Pavement = 3.05 m per lane
Thickness of Pavement = 280 mm
Unit Cost = P1,800 per square meter
It is necessary that the PRC (Point of Reversed Curvature) must be one-fourth the distance BC from B.
- Find the radius of the first curve.
A. 123 m
B. 156 m
C. 182 m
D. 143 m - Find the length of road from A to D. Use arc basis.
A. 552 m
B. 637 m
C. 574 m
D. 468 m - Find the cost of the concrete pavement from A to D.
A. P2.81M
B. P5.54M
C. P3.42M
D. P4.89M
Problem 04 - Symmetrical Parabolic Curve
Problem
A highway engineer must stake a symmetrical vertical curve where an entering grade of +0.80% meets an existing grade of -0.40% at station 10 + 100 which has an elevation of 140.36 m. If the maximum allowable change in grade per 20 m station is -0.20%, what is the length of the vertical curve?
A. 150 m
B. 130 m
C. 120 m
D. 140 m
- Read more about Problem 04 - Symmetrical Parabolic Curve
- Log in or register to post comments
Problem 01 - Symmetrical Parabolic Curve
Problem
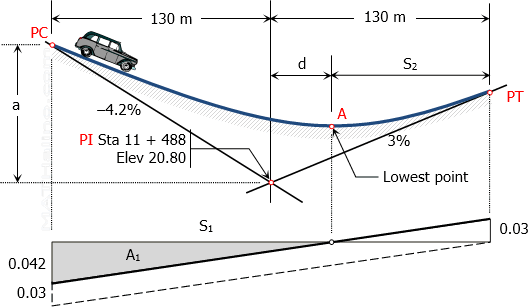
A grade of -4.2% grade intersects a grade of +3.0% at Station 11 + 488.00 of elevations 20.80 meters. These two center gradelines are to be connected by a 260 meter vertical parabolic curve.
- At what station is the cross-drainage pipes be situated?
- If the overall outside dimensions of the reinforced concrete pipe to be installed is 95 cm, and the top of the culvert is 30 cm below the subgrade, what will be the invert elevation at the center?
- Read more about Problem 01 - Symmetrical Parabolic Curve
- Log in or register to post comments