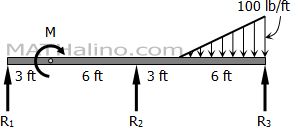
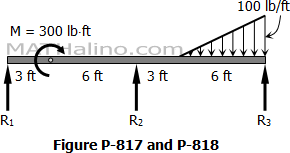
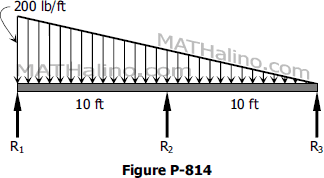
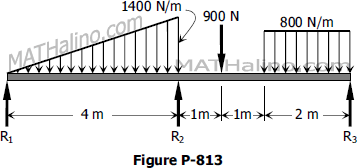
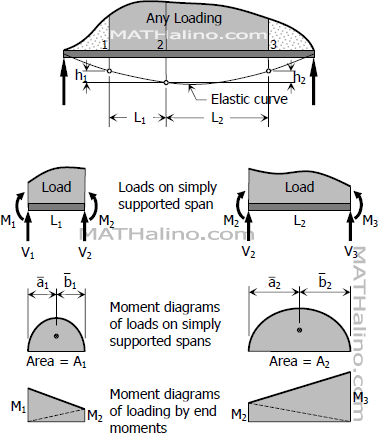
Problem 818 | Continuous Beam by Three-Moment Equation
Problem 818
In Problem 817, determine the changed value of the applied couple that will cause M2 to become zero.
- Read more about Problem 818 | Continuous Beam by Three-Moment Equation
- Log in or register to post comments