Problem 509 | Friction
Problem 509
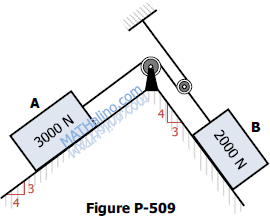
The blocks shown in Fig. P-509 are connected by flexible, inextensible cords passing over frictionless pulleys. At A the coefficients of friction are μs = 0.30 and μk = 0.20 while at B they are μs = 0.40 and μk = 0.30. Compute the magnitude and direction of the friction force acting on each block.
- Read more about Problem 509 | Friction
- Log in or register to post comments