Solution to Problem 347 | Helical Springs
Problem 347
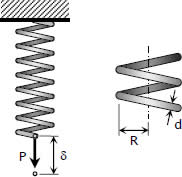
Two steel springs arranged in series as shown in Fig. P-347 supports a load P. The upper spring has 12 turns of 25-mm-diameter wire on a mean radius of 100 mm. The lower spring consists of 10 turns of 20-mm diameter wire on a mean radius of 75 mm. If the maximum shearing stress in either spring must not exceed 200 MPa, compute the maximum value of P and the total elongation of the assembly. Use Eq. (3-10) and G = 83 GPa. Compute the equivalent spring constant by dividing the load by the total elongation.
- Read more about Solution to Problem 347 | Helical Springs
- Log in or register to post comments
Helical Springs
When close-coiled helical spring, composed of a wire of round rod of diameter d wound into a helix of mean radius R with n number of turns, is subjected to an axial load P produces the following stresses and elongation:
The maximum shearing stress is the sum of the direct shearing stress τ1 = P/A and the torsional shearing stress τ2 = Tr/J, with T = PR.
- Read more about Helical Springs
- Log in or register to post comments