Problem 436 - Howe Truss With Counter Braces
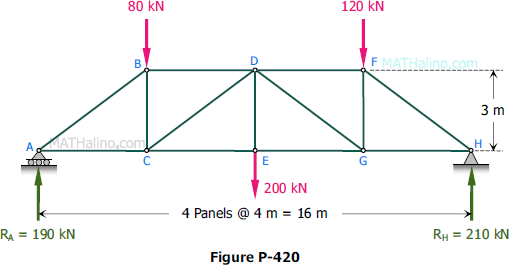
In Figure P-420, assume that counter diagonals act from B to E and from E to F in addition to the counter diagonals CD and DG shown in the figure. Assuming that these counter diagonals can support tension only, determine which diagonals are acting and the force in each.
- Read more about Problem 436 - Howe Truss With Counter Braces
- Log in or register to post comments