Problem 1009 | Width of aluminum plate reinforcement for the wood section to resist 14 kN-m moment
Problem 1009
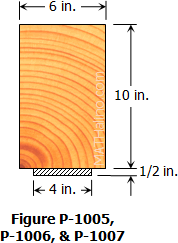
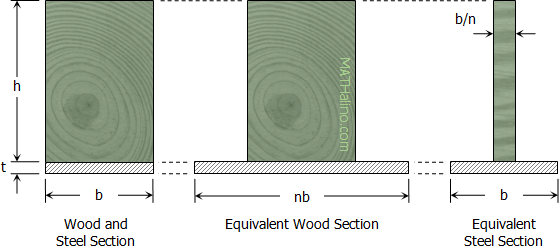
A timber beam 150 mm wide by 200 mm deep is to be reinforced at the top and bottom by aluminum plates 6 mm thick. Determine the width of the aluminum plates if the beam is to resist a moment of 14 kN·m. Assume n = 5 and take the allowable stresses as 10 MPa and 80 MPa in the wood and aluminum, respectively.