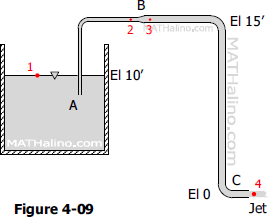
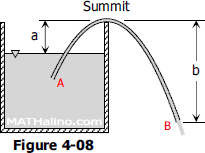
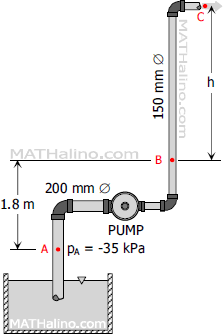
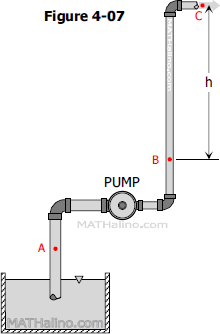
Problem
A conveyor is dispersing sands which forms into a conical pile whose height is approximately 4/3 of its base radius. Determine how fast the volume of the conical sand is changing when the radius of the base is 3 feet, if the rate of change of the radius is 3 inches per minute.
| A. 2π ft/min | C. 3π ft/min |
| B. 4π ft/min | D. 5π ft/min |
- Read more about Rate of Change of Volume of Sand in Conical Shape
- Log in or register to post comments