Combined Axial and Bending
Problem 904 | Combined Axial and Bending
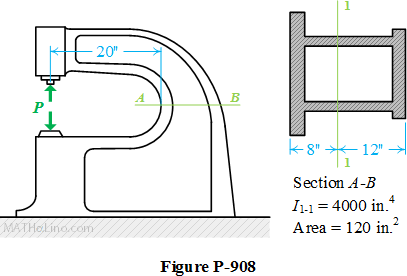
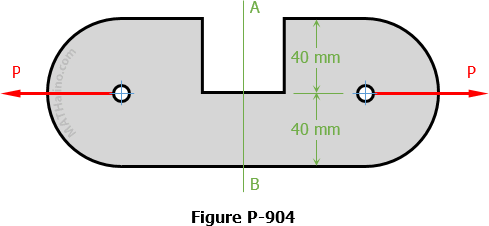
Problem 904
To avoid interference, a link in a machine is designed so that its cross-sectional area is reduced one half at section A-B as shown in Fig. P-904. If the thickness of the link is 50 mm, compute the maximum force P that can be applied if the maximum normal stress on section A-B is limited to 80 MPa.
- Read more about Problem 904 | Combined Axial and Bending
- Log in or register to post comments
Problem 903 | Combined Axial and Bending
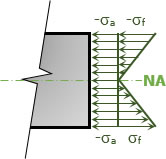
Problem 903
A cast iron link is 40 mm wide by 200 mm high by 500 mm long. The allowable stresses are 40 MPa in tension and 80 MPa in compression. Compute the largest compressive load P that can be applied to the ends of the link along a longitudinal axis that is located 150 mm above the bottom of the link.
- Read more about Problem 903 | Combined Axial and Bending
- Log in or register to post comments