December 2012
Application of Double Integration and Superposition Methods to Restrained Beams
Superposition Method
There are 12 cases listed in the method of superposition for beam deflection.
- Cantilever beam with...
- concentrated load at the free end.
- concentrated load anywhere on the beam.
- uniform load over the entire span.
- triangular load with zero at the free end
- moment load at the free end.
- Simply supported beam with...
- concentrated load at the midspan.
- concentrated load anywhere on the beam span.
- uniform load over the entire span.
- triangular load which is zero at one end and full at the other end.
- triangular load with zero at both ends and full at the midspan.
- moment load at the right support.
- moment load at the left support.
See beam deflection by superposition method for details.
Restrained Beams
Restrained Beams
In addition to the equations of static equilibrium, relations from the geometry of elastic curve are essential to the study of indeterminate beams. Such relations can be obtained from the study of deflection and rotation of beam. This section will focus on two types of indeterminate beams; the propped beams and the fully restrained beams.
- Read more about Restrained Beams
- Log in or register to post comments
Problem 658 | Beam Deflection by Conjugate Beam Method
Problem 658
For the beam shown in Fig. P-658, find the value of EIδ at the point of application of the couple.
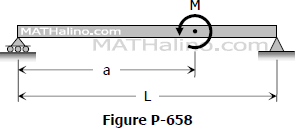
- Read more about Problem 658 | Beam Deflection by Conjugate Beam Method
- Log in or register to post comments
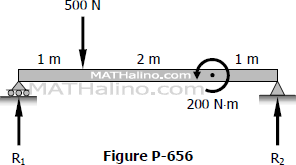
Problem 656 | Beam Deflection by Conjugate Beam Method
Problem 656
Find the value of EIδ at the point of application of the 200 N·m couple in Fig. P-656.
- Read more about Problem 656 | Beam Deflection by Conjugate Beam Method
- Log in or register to post comments
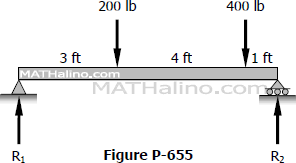
Problem 655 | Beam Deflection by Conjugate Beam Method
Problem 655
Find the value of EIδ under each concentrated load of the beam shown in Fig. P-655.