Problem 539 | Friction on Wedges
Problem 539
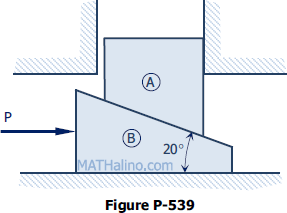
The block A in Fig. P-539 supports a load W = 100 kN and is to be raised by forcing the wedge B under it. The angle of friction for all surfaces in contact is f = 15°. If the wedge had a weight of 40 kN, what value of P would be required (a) to start the wedge under the block and (b) to pull the wedge out from under the block?
- Read more about Problem 539 | Friction on Wedges
- Log in or register to post comments