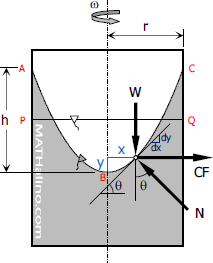
Rotation - Rotating Vessel
When at rest, the surface of mass of liquid is horizontal at PQ as shown in the figure. When this mass of liquid is rotated about a vertical axis at constant angular velocity ω radian per second, it will assume the surface ABC which is parabolic. Every particle is subjected to centripetal force or centrifugal force CF = mω2x which produces centripetal acceleration towards the center of rotation. Other forces that acts are gravity force W = mg and normal force N.
- Read more about Rotation - Rotating Vessel
- Log in or register to post comments