Triangular Load
Solution to Problem 657 | Deflections in Simply Supported Beams
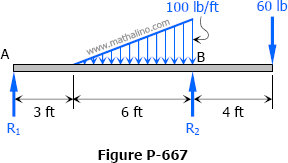
Problem 657
Determine the midspan value of EIδ for the beam shown in Fig. P-657.

Resultant of Parallel Force System
Coplanar Parallel Force System
Parallel forces can be in the same or in opposite directions. The sign of the direction can be chosen arbitrarily, meaning, taking one direction as positive makes the opposite direction negative. The complete definition of the resultant is according to its magnitude, direction, and line of action.
- Read more about Resultant of Parallel Force System
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 648 | Deflection of Cantilever Beams
Problem 648
For the cantilever beam loaded as shown in Fig. P-648, determine the deflection at a distance x from the support.

Solution to Problem 646 | Deflection of Cantilever Beams
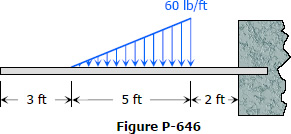
Problem 646
For the beam shown in Fig. P-646, determine the value of I that will limit the maximum deflection to 0.50 in. Assume that E = 1.5 × 106 psi.
Solution to Problem 645 | Deflection of Cantilever Beams
Problem 645
Compute the deflection and slope at a section 3 m from the wall for the beam shown in Fig. P-645. Assume that E = 10 GPa and I = 30 × 106 mm4.

Solution to Problem 629 | Moment Diagrams by Parts
Problem 629
Solve Prob. 628 if the sense of the couple is counterclockwise instead of clockwise as shown in Fig. P-628.

- Read more about Solution to Problem 629 | Moment Diagrams by Parts
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 628 | Moment Diagrams by Parts
Problem 628
For the beam loaded with uniformly varying load and a couple as shown in Fig. P-628 compute the moment of area of the M diagrams between the reactions about both the left and the right reaction.

- Read more about Solution to Problem 628 | Moment Diagrams by Parts
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 627 | Moment Diagram by Parts
Problem 627
For the beam loaded as shown in Fig. P-627compute the moment of area of the M diagrams between the reactions about both the left and the right reaction. (Hint: Resolve the trapezoidal loading into a uniformly distributed load and a uniformly varying load.)

- Read more about Solution to Problem 627 | Moment Diagram by Parts
- Log in or register to post comments
Moment Diagram by Parts
The moment-area method of finding the deflection of a beam will demand the accurate computation of the area of a moment diagram, as well as the moment of such area about any axis. To pave its way, this section will deal on how to draw moment diagram by parts and to calculate the moment of such diagrams about a specified axis.
- Read more about Moment Diagram by Parts
- 2 comments
- Log in or register to post comments