Strength of Materials
Situation
A 12-m pole is fixed at its base and is subjected to uniform lateral load of 600 N/m. The pole is made-up of hollow steel tube 273 mm in outside diameter and 9 mm thick.
1. Calculate the maximum shear stress (MPa).
| A. 0.96 | C. 1.39 |
| B. 1.93 | D. 0.69 |
2. Calculate the maximum tensile stress (MPa).
| A. 96.0 | C. 60.9 |
| B. 69.0 | D. 90.6 |
3. Calculate the force (kN) required at the free end to restrain the displacement.
| A. 2.7 | C. 27 |
| B. 7.2 | D. 72 |
- Read more about Stresses of Hollow Circular Tube Used as a Pole
- Log in or register to post comments
Situation
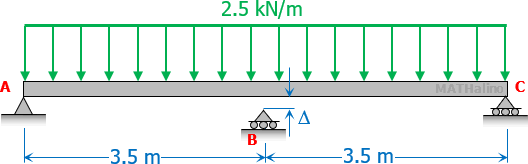
A beam of uniform cross section whose flexural rigidity EI = 2.8 × 1011 N·mm2, is placed on three supports as shown. Support B is at small gap Δ so that the moment at B is zero.
1. Calculate the reaction at A.
| A. 4.375 kN | C. 5.437 kN |
| B. 8.750 kN | D. 6.626 kN |
2. What is the reaction at B?
| A. 4.375 kN | C. 5.437 kN |
| B. 8.750 kN | D. 6.626 kN |
3. Find the value of Δ.
| A. 46 mm | C. 34 mm |
| B. 64 mm | D. 56 mm |
Situation
A temporary earth retaining wall consists of wooden plank driven vertically into the ground. The wall is designed to resist 2.4 m height of soil.
Cross-sectional dimensions of the plank = 300 mm wide × 75 mm thick
Allowable bending stress of the plank = 10.4 MPa
Allowable shear stress of the plank = 0.8 MPa
Unit weight of retained soil = 17.3 kN/m3
Active earth pressure coefficient = 1/3
1. Calculate the maximum flexural stress.
| A. 12.7 MPa | C. 8.6 MPa |
| B. 14.2 MPa | D. 10.1 MPa |
2. Calculate the maximum shear stress.
| A. 1.11 MPa | C. 0.99 MPa |
| B. 0.33 MPa | D. 0.77 MPa |
3. Calculate the minimum thickness of the plank to prevent failure.
| A. 90 mm | C. 110 mm |
| B. 80 mm | D. 100 mm |