Problem 361 | Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent Force System
Problem 361
Referring to Problem 359, if T = 30 kN and x = 1 m, determine the angle θ at which the bar will be inclined to the horizontal when it is in a position of equilibrium.

Problem 361
Referring to Problem 359, if T = 30 kN and x = 1 m, determine the angle θ at which the bar will be inclined to the horizontal when it is in a position of equilibrium.

Problem 360
Referring to Problem 359, what value of T acting at x = 1 m from B will keep the bar horizontal.

Problem 359
A 4-m bar of negligible weight rests in a horizontal position on the smooth planes shown in Fig. P-359. Compute the distance x at which load T = 10 kN should be placed from point B to keep the bar horizontal.

Problem 358
A bar AE is in equilibrium under the action of the five forces shown in Fig. P-358. Determine P, R, and T.

Problem 349
A rigid bar, hinged at one end, is supported by two identical springs as shown in Fig. P-349. Each spring consists of 20 turns of 10-mm wire having a mean diameter of 150 mm. Compute the maximum shearing stress in the springs, using Eq. (3-9). Neglect the mass of the rigid bar.
Problem 272
For the assembly in Fig. 271, find the stress in each rod if the temperature rises 30°C after a load W = 120 kN is applied.
Problem 271
A rigid bar of negligible weight is supported as shown in Fig. P-271. If W = 80 kN, compute the temperature change that will cause the stress in the steel rod to be 55 MPa. Assume the coefficients of linear expansion are 11.7 µm/(m·°C) for steel and 18.9 µm/(m·°C) for bronze.
Problem 254
As shown in Fig. P-254, a rigid bar with negligible mass is pinned at O and attached to two vertical rods. Assuming that the rods were initially stress-free, what maximum load P can be applied without exceeding stresses of 150 MPa in the steel rod and 70 MPa in the bronze rod.

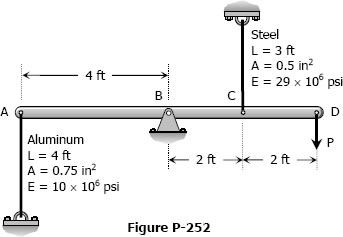
Problem 252
The light rigid bar ABCD shown in Fig. P-252 is pinned at B and connected to two vertical rods. Assuming that the bar was initially horizontal and the rods stress-free, determine the stress in each rod after the load after the load P = 20 kips is applied.
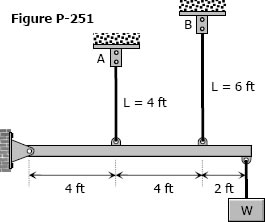
Problem 251
The two vertical rods attached to the light rigid bar in Fig. P-251 are identical except for length. Before the load W was attached, the bar was horizontal and the rods were stress-free. Determine the load in each rod if W = 6600 lb.