Problem 20 - Bernoulli's Energy Theorem
Problem 20
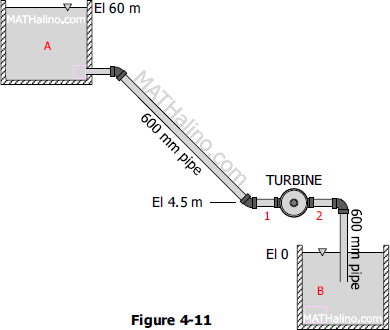
The 600-mm pipe shown in Figure 4-11 conducts water from reservoir A to a pressure turbine, which discharges through another 600-mm pipe into tailrace B. The loss of head from A to 1 is 5 times the velocity head in the pipe and the loss of head from 2 to B is 0.2 times the velocity head in the pipe. If the discharge is 700 L/s, what power is being given up by the water to the turbine and what are the pressure heads at 1 and 2?
- Read more about Problem 20 - Bernoulli's Energy Theorem
- Log in or register to post comments