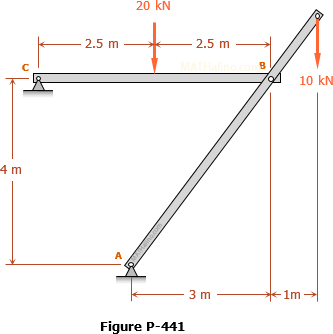
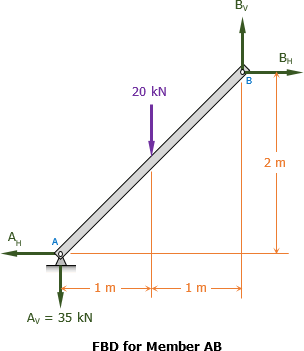
method of members
Problem 004-mm | Method of Members
Problem 004-mm
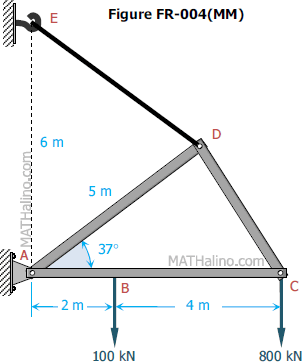
For the structure shown in Fig. FR-004(MM), members AD, DC, and ABC are assumed to be solid rigid members; member ED is a cable. For this structure, determine the reaction at A, the tension on cable ED, and the force in member DC.
- Read more about Problem 004-mm | Method of Members
- Log in or register to post comments
Method of Members | Frames Containing Three-Force Members
A three-force member is in general a non-axial member that is not simply in tension or compression. A member of this kind has shear forces perpendicular to the member and subjected to bending loads. If forces are applied to more than two positions on the member, it is three-force member. Any beam is a three-force member according to the above definition.
Frames are pin-connected structures with some or all members are three-force members. To analyze a frame, we can disconnect the three-force member from the structure and draw the free-body diagram of the member. This approach is called the method of members.