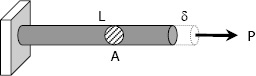
Axial Deformation
In the linear portion of the stress-strain diagram, the tress is proportional to strain and is given by
$\sigma = E \varepsilon$
since $\sigma = P / A$ and $\varepsilon = \delta / L$, then $\dfrac{P}{A} = E \dfrac{\delta}{L}$
$\delta = \dfrac{PL}{AE} = \dfrac{\sigma L}{E}$
To use this formula, the load must be axial, the bar must have a uniform cross-sectional area, and the stress must not exceed the proportional limit.
- Read more about Axial Deformation
- Log in or register to post comments
Simple Strain
Also known as unit deformation, strain is the ratio of the change in length caused by the applied force, to the original length.
$\varepsilon = \dfrac{\delta}{L}$
where δ is the deformation and L is the original length, thus ε is dimensionless.
- Read more about Simple Strain
- Log in or register to post comments
