Solution to Problem 111 Normal Stress
Problem 111
For the truss shown in Fig. P-111, calculate the stresses in members CE, DE, and DF. The cross-sectional area of each member is 1.8 in2. Indicate tension (T) or compression (C).
- Read more about Solution to Problem 111 Normal Stress
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 110 Normal Stress
Problem 110
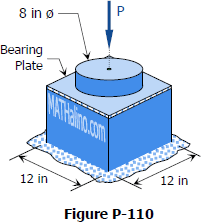 A 12-inches square steel bearing plate lies between an 8-inches diameter wooden post and a concrete footing as shown in Fig. P-110. Determine the maximum value of the load P if the stress in wood is limited to 1800 psi and that in concrete to 650 psi.
A 12-inches square steel bearing plate lies between an 8-inches diameter wooden post and a concrete footing as shown in Fig. P-110. Determine the maximum value of the load P if the stress in wood is limited to 1800 psi and that in concrete to 650 psi.
- Read more about Solution to Problem 110 Normal Stress
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 109 Normal Stress
Problem 109
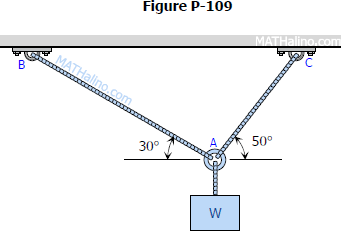
Determine the largest weight W that can be supported by two wires shown in Fig. P-109. The stress in either wire is not to exceed 30 ksi. The cross-sectional areas of wires AB and AC are 0.4 in2 and 0.5 in2, respectively.
- Read more about Solution to Problem 109 Normal Stress
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 108 Normal Stress
Problem 108
An aluminum rod is rigidly attached between a steel rod and a bronze rod as shown in Fig. P-108. Axial loads are applied at the positions indicated. Find the maximum value of P that will not exceed a stress in steel of 140 MPa, in aluminum of 90 MPa, or in bronze of 100 MPa.
- Read more about Solution to Problem 108 Normal Stress
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 107 Normal Stress
Problem 107
A rod is composed of an aluminum section rigidly attached between steel and bronze sections, as shown in Fig. P-107. Axial loads are applied at the positions indicated. If P = 3000 lb and the cross sectional area of the rod is 0.5 in2, determine the stress in each section.

- Read more about Solution to Problem 107 Normal Stress
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 105 | Normal Stress
Problem 105
A homogeneous 800 kg bar AB is supported at either end by a cable as shown in Fig. P-105. Calculate the smallest area of each cable if the stress is not to exceed 90 MPa in bronze and 120 MPa in steel.
- Read more about Solution to Problem 105 | Normal Stress
- Log in or register to post comments
Simple Stresses
Simple Stresses
- Normal Stress
- Shear Stress
- Bearing Stress
- Thin-walled Pressure Vessel
- Read more about Simple Stresses
- Log in or register to post comments
Solution to Problem 104 Normal Stress
Problem 104
A hollow steel tube with an inside diameter of 100 mm must carry a tensile load of 400 kN. Determine the outside diameter of the tube if the stress is limited to 120 MN/m2.
- Read more about Solution to Problem 104 Normal Stress
- 2 comments
- Log in or register to post comments