frame
Problem 006-fr | Analysis of Simple Frame
Problem 006-fr
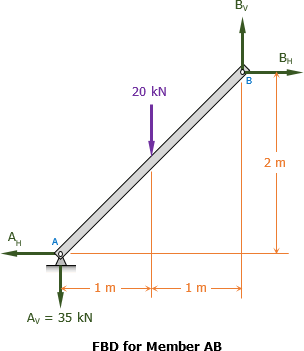
In the structure shown in Fig. P-006(FR-H), all members are assumed to be solid rigid members. The system is pinned to the wall at point A and supported by a roller at point E. Calculate the force on member BD and the reactions at A and E.
- Read more about Problem 006-fr | Analysis of Simple Frame
- Log in or register to post comments
Method of Members | Frames Containing Three-Force Members
A three-force member is in general a non-axial member that is not simply in tension or compression. A member of this kind has shear forces perpendicular to the member and subjected to bending loads. If forces are applied to more than two positions on the member, it is three-force member. Any beam is a three-force member according to the above definition.
Frames are pin-connected structures with some or all members are three-force members. To analyze a frame, we can disconnect the three-force member from the structure and draw the free-body diagram of the member. This approach is called the method of members.
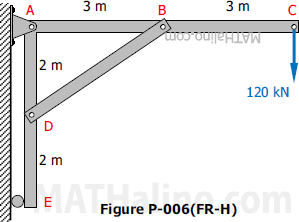
Problem 348 | Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent Force System
Problem 348
The frame shown in Fig. P-348 is supported in pivots at A and B. Each member weighs 5 kN/m. Compute the horizontal reaction at A and the horizontal and vertical components of the reaction at B.
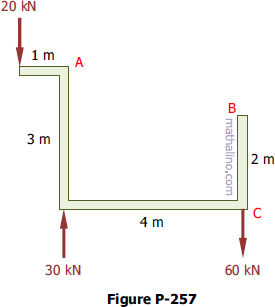
257 Horizontal couple equivalent to vertical forces
Problem 257
Replace the system of forces acting on the frame in Fig. P-257 by a resultant R at A and a couple acting horizontally through B and C.
- Read more about 257 Horizontal couple equivalent to vertical forces
- Log in or register to post comments
017 Computation of force with given component parallel to a frame member
Problem 017
If the force F shown in Fig. P-017 is resolved into components parallel to the bars AB and BC, the magnitude of the component parallel to bar BC is 4 kN. What are the magnitudes of F and its component parallel to AB?